Just published my latest article on Impakter magazine, here's the opening:
As our environment is undergoing ever faster collapse, with the rainforest burning in the Amazon, the ice melting in the Arctic and now California ravaged by fires, the goal of achieving sustainable finance appears ever more elusive. It is obvious that nature risks directly translate into financial risks. And with climate change accelerating, it is equally obvious that growing natural risks is the cause of equally growing financial instability.
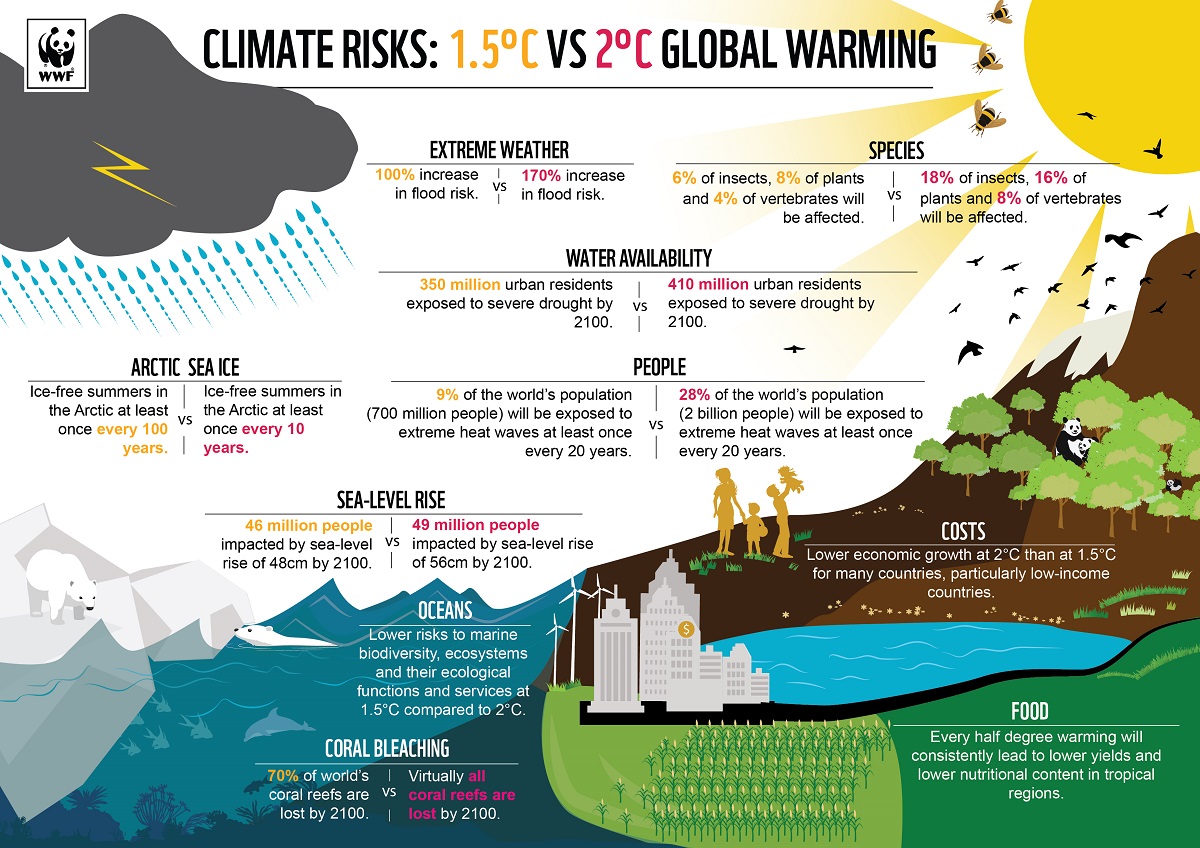
While the relation between nature, climate and sustainable finance is obvious, the exact impact is not so clear. Natural disasters, from floods to air pollution events to wildlife species extinction, can impact businesses and whole economic sectors in variable ways, some more than others. And a small further rise in global warming, as small as a half degree centigrade, can make a stunningly huge difference:
To illustrate with the famous case of a highly valuable wildlife species threatened by extinction, i.e. bees whose pollination activities are fundamental for agricultural production. A prosperous European pharmaceutical company suddenly faced catastrophic financial losses after it had acquired in 2018 an agrochemical company accused of causing adverse impacts on bee populations that led to a series of health-related trials. Suddenly, it lost almost 40% of its market capitalization in less than one year, causing shareholders billions in losses.
To put a name on these firms: the pharmaceutical company is Bayer, the agrochemical is Monsanto and the cause of the bee-killing is, of course, a pesticide, the infamous “Roundup”. In short, Bayer is worth less today than the $63 billion it paid for Monsanto about a year ago.
As a first step to ascertain what the effects of nature risks are on the finance industry, a number of academics at the University of Hamburg have formed a Research Group on Sustainable Finance and analysed for the first time the existing academic literature which highlighted the relationship between nature risks and financial risks. The study has been financed by WWF Switzerland and will be uploaded to their website this month.
They identified 154 peer-reviewed articles published between 1966 and 2019. These articles covered four areas: banking, insurance, real estate, and stock markets; and nine nature risks: disease, drought, erosion, flooding, invasive species, oil spills, pollution/environmental contamination - of air, groundwater, soil/land and surface water -, solid waste, and bushfires.
Incorrect pricing is a major concern. It means that financial institutions urgently need to identify how the activities they finance impact the natural world. Developing a framework for investors to analyse nature risks and integrating these systematically in their valuation models is crucial. It would be the first indispensable step to achieve sustainable finance.
What is interesting is how the literature reviewed by the Research Group on Sustainable Finance identified variable impacts depending on the sector and the kind of nature risk. The sector that tends to suffer the most from nature risks is real estate. The greatest threats to valuation in the real estate sector include flooding followed by air pollution (and environmental contamination in general) and bushfires.
That of course, is a massive financial problem – but it is a problem for individual property owners too. The house you just bought, or that you inherited from your parents, could be worth next to nothing in just a few short years.
...
To find out how other sectors in the economy will be impacted and what should be done, read the rest on Impakter, click here: https://impakter.com/sustainable-finance-address-nature-risks-climate-change/
SUSTAINABLE FINANCE: HOW TO ADDRESS NATURE RISKS AND CLIMATE CHANGE
As our environment is undergoing ever faster collapse, with the rainforest burning in the Amazon, the ice melting in the Arctic and now California ravaged by fires, the goal of achieving sustainable finance appears ever more elusive. It is obvious that nature risks directly translate into financial risks. And with climate change accelerating, it is equally obvious that growing natural risks is the cause of equally growing financial instability.
While the relation between nature, climate and sustainable finance is obvious, the exact impact is not so clear. Natural disasters, from floods to air pollution events to wildlife species extinction, can impact businesses and whole economic sectors in variable ways, some more than others. And a small further rise in global warming, as small as a half degree centigrade, can make a stunningly huge difference:
To illustrate with the famous case of a highly valuable wildlife species threatened by extinction, i.e. bees whose pollination activities are fundamental for agricultural production. A prosperous European pharmaceutical company suddenly faced catastrophic financial losses after it had acquired in 2018 an agrochemical company accused of causing adverse impacts on bee populations that led to a series of health-related trials. Suddenly, it lost almost 40% of its market capitalization in less than one year, causing shareholders billions in losses.
To put a name on these firms: the pharmaceutical company is Bayer, the agrochemical is Monsanto and the cause of the bee-killing is, of course, a pesticide, the infamous “Roundup”. In short, Bayer is worth less today than the $63 billion it paid for Monsanto about a year ago.
As a first step to ascertain what the effects of nature risks are on the finance industry, a number of academics at the University of Hamburg have formed a Research Group on Sustainable Finance and analysed for the first time the existing academic literature which highlighted the relationship between nature risks and financial risks. The study has been financed by WWF Switzerland and will be uploaded to their website this month.
They identified 154 peer-reviewed articles published between 1966 and 2019. These articles covered four areas: banking, insurance, real estate, and stock markets; and nine nature risks: disease, drought, erosion, flooding, invasive species, oil spills, pollution/environmental contamination - of air, groundwater, soil/land and surface water -, solid waste, and bushfires.
Overall, the articles confirmed that the destruction of ecosystems results in financial risks. They also found that nature risks are not adequately reflected in current risk models of financial institutions and therefore not priced correctly."Destruction of ecosystems results in financial risks"
Incorrect pricing is a major concern. It means that financial institutions urgently need to identify how the activities they finance impact the natural world. Developing a framework for investors to analyse nature risks and integrating these systematically in their valuation models is crucial. It would be the first indispensable step to achieve sustainable finance.
What is interesting is how the literature reviewed by the Research Group on Sustainable Finance identified variable impacts depending on the sector and the kind of nature risk. The sector that tends to suffer the most from nature risks is real estate. The greatest threats to valuation in the real estate sector include flooding followed by air pollution (and environmental contamination in general) and bushfires.
That of course, is a massive financial problem – but it is a problem for individual property owners too. The house you just bought, or that you inherited from your parents, could be worth next to nothing in just a few short years.
...
To find out how other sectors in the economy will be impacted and what should be done, read the rest on Impakter, click here: https://impakter.com/sustainable-finance-address-nature-risks-climate-change/

Comments